9.3 Instructions
One of the most common and important uses of technical writing is to provide instructions, those step-by-step explanations of how to assemble, operate, repair, or do routine maintenance on equipment or other objects. At other times, you may need to use brief instructions or direction as you interact with an LLM. Instructions are step-by-step explanations of how to use equipment, perform a task, complete forms, comply with policies, or perform other procedures. For example, you might see instructions during safety training when you are first hired. Or you might see instructions when you first learn to use a tool. Instructions also often accompany new products that are purchased by customers and industry partners. These documents are essential in helping the user to make the most of their purchase and of their time.
Instructions serve many purposes and come in many forms:
- short emails
- standard operating procedures
- employee training
- demonstrations
- manuals
- user guides
- pamphlets
- webinars
- video tutorials
- LLM prompting
An effective set of instructions requires the following:
- clear, precise, and straight-forward writing
- a thorough understanding of the procedure in all its technical detail
- the ability to put yourself in the place of the reader, the person trying to use your instructions
- the ability to visualize the procedure in detail and to capture that awareness in the steps provided
- willingness to test your instructions on the kind of person you wrote them for
Although they may seem intuitive and simple to write, instructions are some of the worst-written documents you can find. Most of us have probably had many infuriating experiences with badly written instructions. This chapter will introduce genAI applications that can facilitate instruction development and discuss the features of instructions that promote readability.
Take a look at this University of Minnesota video that offers a good overview of instructions from content and stylistic perspectives.
(Instruction Documents, 2013)
AI-Assisted Instruction Creation
AI Instruction creators will create any set of instructions with information you provide. Information can be uploaded in the form of drafts, reference documents, regulations, policies, as well as videos of the performance of tasks and the verbal narration of tasks. Most instruction generators will also capture screen recordings of tasks while they are being performed on computers. Depending on the generator, the instructions it creates will be accompanied with photos or diagrams to illustrate the process. Some generators will also provide voice narration in any number of languages. AI instruction creators are powerful applications that can save you lots of time. Many offer the following features and capabilities (McFarland, 2024, Guidde, ClickUp, Whale, Scribe):
Use of reference documents: Many instruction generators will allow users to upload reference documents like policies and guides. The generator will use these to create a knowledge base upon which it will draw information to ensure that the processes align with those guidelines. In addition, some generators will create the instructions based on brief prompting, drafts, or outlines.
Workflow capture: Most instruction generators will record or take screenshots of a workflow as it is occurring on the computer. It will then use the information to generate the set of instructions, demonstration, video tutorial or other asset. Other generators like Whale will allow users to upload a video, which will be analyzed to capture the procedure using text and images. And ClickUp enables the use of voice to text to create the workflow description.
Multimedia formats: Many instruction creators will create multimedia components to support the text-based documentation. To support employees in their workflows, videos, diagrams, photos, flowcharts and the like can become part of the instructions. Notably, voice narrations of processes can be completed in any number of languages as needed.
Dynamic revisions and tracking: Some instruction creators will enable real-time editing and updating of the documentation. In addition, the applications will allow for role-defined collaboration in the process of review, testing, and approval. Many instruction generators will also feature real time tracking of employees who have read and/or who are using the documentation to perform tasks.
Use of templates: Some instruction generators will have a range of industry-specific and purpose-related templates allowing for the more rapid development of content and organization.
Voice-to-text capabilities: For employees working in hands-on environments like construction, manufacturing, and assembly, or out in the field, some instruction generators will have voice-to-text capabilities so that the procedure can be captured verbally as it is in process. The generator will then take the information shared by voice and convert it to text and video. See ClickUp for an example of such an application.
Assets Created: Instruction generators are capable of using all documentation uploaded including video, voice, and images, as well as the instructions they create to then rapidly develop various assets including: training modules, quizzes, demonstrations, webinars, video tutorials, and consumer guides and instructions. Any of these serve various purposes but combine to create a wealth of information for employees and customers to ensure that they are familiar with the procedures.
While these AI instruction generators offer many conveniences, remember to always check the contents of the instructions, whether they are in the form of video or text, to ensure their accuracy and completeness. In technology, instructions, as with SOPs, are critical documents in guiding employees and customers in the correct performance of tasks. Your organization could be held liable for legal damages if any injury, equipment failures, and other damages occur through the use of the instructions.
But what’s involved in creating reliable, accurate, and complete instruction for which safety is top of mind? Read on.
Getting Organized
At the beginning of a project to write a set of instructions, whether you are using an AI tool or completing the work without, begin by determining the focus, structure, and characteristics of the particular procedure you are going to write about. Here are some steps to follow:
1. Do a careful audience analysis
Early in the process, define the audience and situation for your instructions. Remember that defining an audience means defining the level of familiarity your readers have with the topic and the context within which they will be using the instructions: office, shop floor, field, retail, general public, etc. Envision your real audience, not your ideal one. A real audience is one that would use the instructions in ways that would be specific to their context and need. An ideal audience is one we imagine to be perfect users of the instructions. Focusing on the real audience will help you focus on the content that a reader would need in the context or location where the instructions would typically be used.
Delegating audience analysis to an LLM is tempting, but would only be practicable if that audience is more broad or general or public in nature. If you are writing instructions for a small, local audience, say a colleague, the LLM would not be of much help because only you would have the insights into the needs and context of that smaller and local audience; whereas, it would be impossible for the LLM to have that information. For broader audiences, once you have competed the analysis, tell the LLM how you envision your audience and ask it to add any detail that it can to create a more complete profile.
2. Do a thorough task analysis
Let’s use the term procedure to refer to the whole set of activities your instructions are intended to discuss. A task is a semi-independent group of actions within the procedure: For example, setting the clock on a microwave oven is one task in the big overall procedure of operating a microwave oven.
What tasks are involved in the entire procedure?
• Complete a thorough task analysis by performing the task yourself, if possible
• Group related tasks together
• Determine the number of tasks and identify phases
LLMs and AI instruction creators can draft a task analysis for almost any process that is publicly known. For example, you can ask an LLM to give you a task analysis for setting up video meeting equipment in a room for 30 people, and it will give you a list of tasks involved in the process. If, however, you are working, say, in research and development and have invented a brand new technology or mechanism that has not as yet been made available anywhere or promoted on the internet, then the LLM would have no knowledge about the object and would not be able to help you much with the task analysis. In short, you have to use your judgement as to when you can delegate a task analysis to an LLM.
3. Determine the best approach for the steps
For most instructions, you can focus on tasks, or you can focus on tools (or features of tools). In a task approach (also known as task orientation) for instructions on using a phone-answering service, for example, you would include these sections:
- Recording your greeting
- Playing back your messages
- Saving your messages
- Forwarding your messages
- Deleting your messages, and so on
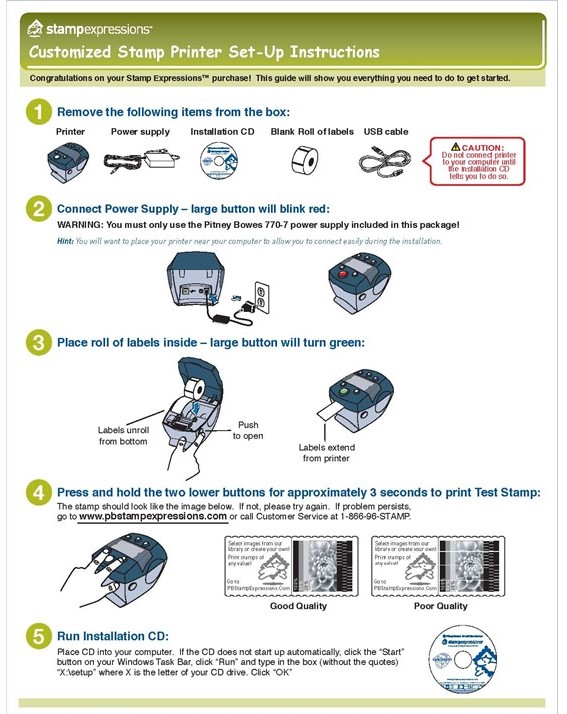
These are tasks—the typical things we’d want to do with the machine. See Figure 9.3.1 for an example of instructions written using the task approach
On the other hand, in a tools approach to instructions on using a photocopier, there likely would be sections on how to use specific features:
- Copy button
- Cancel button
- Enlarge/reduce button
- Collate/staple button
- Copy-size button, and so on
If you designed a set of instructions along this plan, you would include steps for using each button or feature of the photocopier. Instructions using this tools approach, however, are hard to make work. Sometimes, the name of the button doesn’t quite match the task it is associated with; sometimes you have to use more than just one button to accomplish the task. Nevertheless, there can be times when the tools/feature approach may be preferable, so being aware of this approach can prove to be useful even if it isn’t used often.
4. Design groupings of tasks

Some instructions have only a single task but have many steps within that single task. For example, imagine a set of instructions for assembling a kids’ swing set. There can be more than 130 steps in the process, which can be a bit daunting. A useful approach is to group similar and related steps into phases, and start renumbering the steps at each new phase. A phase then is a group of similar steps within a single-task procedure. In the swing-set example, setting up the frame would be a phase; anchoring the thing in the ground would be another; assembling the box swing would be still another.
Another example would group common technical tasks as follows:
-
- Unpacking and setup tasks
- Installing and customizing tasks
- Basic operating tasks
- Routine maintenance tasks
- Troubleshooting tasks
An AI-assisted instruction creator would automatically group tasks. However, if you are working with an LLM, it can help you group a complex sequence of tasks. Here is an example of how to do that:
Asking an LLM to Help You Group Tasks
Prompt
I am writing a set of instructions on how to [name the overall procedure]. Begin by helping me brainstorm all the steps involved in the process.
You would then review the list of steps to be sure that they are accurate and complete. Any missing steps will result in a poor set of instructions, so be sure to add those that are required.
Note: The LLM may give you a segmented list of tasks. If this is the case, you would not have to proceed with the following, but you would have to ensure that all tasks are effectively organized.
This list of steps may be too long for the reader. Would you please help me group the tasks or steps so that they are categorized according to main phases for the process. For example, the process of making breakfast would begin with the first phase, which involves “making toast”: 1) getting the bread from the fridge, 2) placing a slice in the toaster, 3) adjusting the heat, 4) dropping the lever for toasting, and 5) waiting until the lever rises to obtain the toast. Each phase or category should include about 3-5 steps. I will be numbering the sequences using an numeric method.
Knowledge Check
Segmenting Content
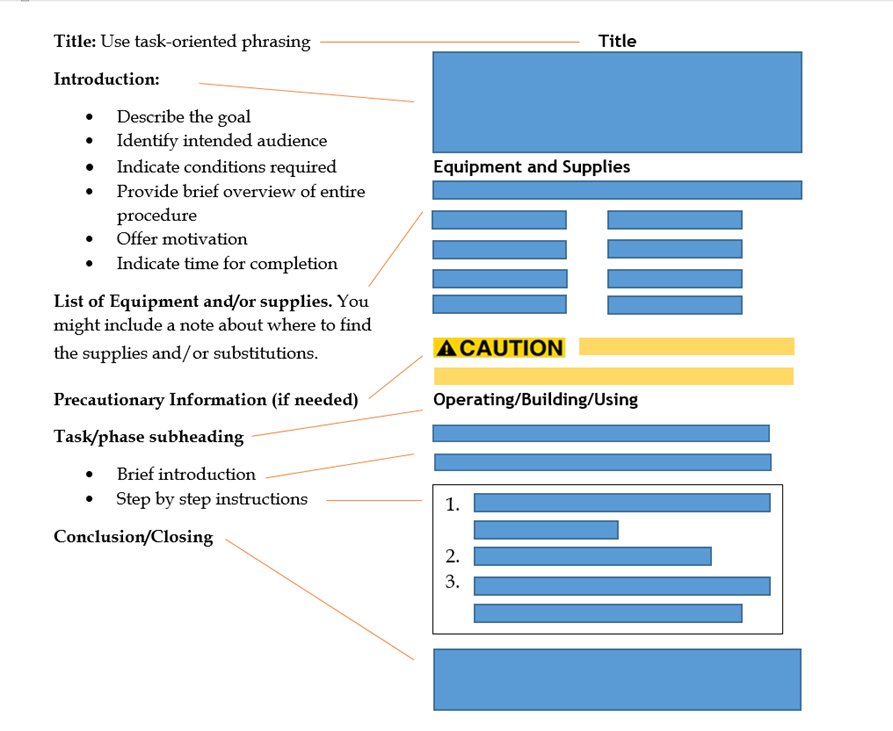
When working with an AI instruction generator, it will automatically create the sections that work with the information you provide about subject, audience, context, and purpose. Regardless of your use of such tools, however, you still have to know what goes into an instruction document so you can appropriately guide the generator or LLM. The following is an overview of the sections you’ll commonly find in instructions. Don’t assume, however, that each one of them must be in the actual instructions you write, nor that they have to be in the order presented here, nor that these are the only sections possible in a set of instructions. Always consider your audience and context first, then adapt your document accordingly.
For alternative formats, check out David McMurrey’s Sample Instructions.
Introduction: The introduction might include any of the following (but not necessarily in this order):
- The specific tasks or procedure to be explained as well as the scope (what will and will not be covered).
- The audience requirements in terms of knowledge and background to understand the instructions.
- A general idea of the procedure and what it accomplishes.
- The conditions when these instructions should (or should not) be used.
- An overview of the contents of the instructions.
General warning, caution, danger notices: Instructions often must alert readers to the possibility of ruining their equipment, compromising the procedure, and hurting themselves. Also, instructions must often emphasize key points or exceptions. For these situations, you use special notices—general notes, warnings, caution, and danger notices. General warning, caution, and danger notes will appear following the Introduction, and specific notices will appear immediately before any relevant step. When a procedure involves any hazard to humans or animals, or potential for damage, you have a legal and moral responsibility to include these special notices in the opening and in the discussion of steps in your document.
Technical background or theory: At the beginning of certain kinds of instructions (after the introduction), background information related to the procedure could be helpful for the reader. For other instructions, this background is critical; otherwise, the steps in the procedure would make no sense.
- In technical contexts, reference to codes, regulations, manufacturer’s datasheets, and other technical documents are required.
- Background on specific knowledge or skills required to perform the tasks should also be included.
For example, you may have had some experience with those software applets in which you define your own colors by nudging red, green, and blue slider bars around. To really understand what they’re doing, the audience would need to have some background on color. Similarly, you can imagine that, for certain instructions on using cameras, some theory might be needed as well.
Equipment and supplies: Notice that most instructions include a list of the things you need to gather before you start the procedure. This includes equipment, the tools used in the procedure (such as mixing machines, hammers, drills, and saws) and supplies, the things that are consumed in the procedure (such as wood, paint, and nails). Be sure to include any personal protective equipment (PPE) (such as protective masks, steel-toed boots, gloves, and goggles), as this equipment is essential to protect readers when following instructions that may involve hazards. In instructions, these typically are listed either in a simple vertical list or in a two-column list. A two-column list works best if you need to add some specifications to some or all of the items—for example, brand names, sizes, amounts, types, model numbers, and so on.
Discussion of the steps: For the steps, keep in mind the following: 1) the structure and format of those steps, 2) supplementary information that might be needed, and 3) the point of view and general writing style.
Include a specific note, caution, danger, and warning notices before each relevant step. Placement before the step is the most logical place because you would not want someone to go ahead and perform a hazardous step without first reading the warning, caution, or danger note. Notice how these special notices are used in the McMurrey sample instructions.
Structure and format: Normally, we imagine a set of instructions as being formatted as vertical numbered lists. And most are as such. There are some variations, however, as well as some other considerations:
- Fixed-order steps are steps that must be performed in the order presented. For example, if you are changing the oil in a car, draining the oil is a step that must come before putting in the new oil. These are numbered lists (usually, vertical numbered lists).
- Variable-order steps are steps that can be performed in practically any order. Good examples are those troubleshooting guides that tell you to check this and check that when you are trying to fix something. You can perform these kinds of steps in practically any order. With this type, the bulleted list is the appropriate format.
- Alternate steps are those in which two or more ways to accomplish the same step are presented. Alternate steps are also used when various conditions might exist. Use nested bulleted lists with this type, with OR inserted between the alternatives, or include a lead-in indicating that alternatives are about to be presented.
- Nested steps may be used in cases when individual steps within a procedure are rather complex in their own right and need to be broken down into sub-steps. In this case, you indent further and sequence the sub-steps using the appropriate numbering.
- “Step-less” instructions can be used when you really cannot use numbered vertical list or provide straightforward instructional-style directing of the reader. Some situations must be so generalized or so variable that steps cannot be stated.
Supplementary discussion: Often, it is not enough simply to tell readers to do this or to do that. They need additional explanatory information such as how the thing should look before and after the step; why they should care about doing this step; what mechanical principle is behind what they are doing; even more micro-level explanation of the step—discussion of the specific actions that make up the step.
The problem with supplementary discussion, however, is that it can hide the actual step. You want the actual step—the specific actions the reader is to take—to stand out. You don’t want it all buried in a heap of words. There are at least two techniques to avoid this problem: you can split the instruction from the supplement into separate paragraphs; or you can bold the instruction.
See Figure 9.3.3 for an illustration of how such sections can be organized.
Figure 9.3.3 An example of how instructions can be written. Remember to see the link above for alternatives (Beilfus, n.d.).
Knowledge Check
Using Instruction Style Conventions
Most LLMs and AI instruction generators will stylize the language using the conventions for instructions. Instructions are most commonly conveyed using the active voice because the passive voice in instructions can be problematic. For some strange reason, some instructions sound like this: “The Pause button should be depressed in order to stop the display temporarily.” Not only are we worried about the pause button’s mental health, but we wonder who’s supposed to depress the thing (ninjas?). It would be more helpful to indicate when the reader must “press the Pause button.” Consider this example: “The Timer button is then set to 3:00.” Again, one might ask, “is set by whom? Ninjas?” The person following these instructions might think it is simply a reference to some existing state, or she might wonder, “Are they talking to me?” Using the third person can also lead to awkwardness: “The user should then press the Pause button.”
Instructions should typically be written using command verb forms in the active voice (also known as the imperative mood) and using “you” to make it perfectly clear what the reader should do. Here is an example:
Step 2: Inflating your automobile tires with air
2.1. After driving to the service station, locate the air compressor and park the car next to it.
2.2. Remove the valve stem caps on all four tires.
2.3. Check the PSI number for your vehicle’s tires.
2.4. Turn on the air compressor. (Insert sufficient coinage if necessary).
CAUTION: Do not over-inflate your tires. Doing so will result in faster tread wear and tear.
2.5. Inflate each tire with air from the compressor.
2.6. Check the tire pressure (or PSI) of each tire and adjust using the tire gauge.
2.7. Recap each valve with the valve stem caps.
Note: Each step (except for step 1) begins with a verb in the present tense–the imperative mood. Step 2.1, begins with a qualifier: “After driving to the service station. . .” The step then goes on to use a command style to explain the step.
Also, note the numbering: In technical instructions, use this numerical method for indicating the section or phase each step belongs to. For example, Step 2.1 belongs to Section 2.
Example created by Robin L. Potter
Illustrating Your Instructions
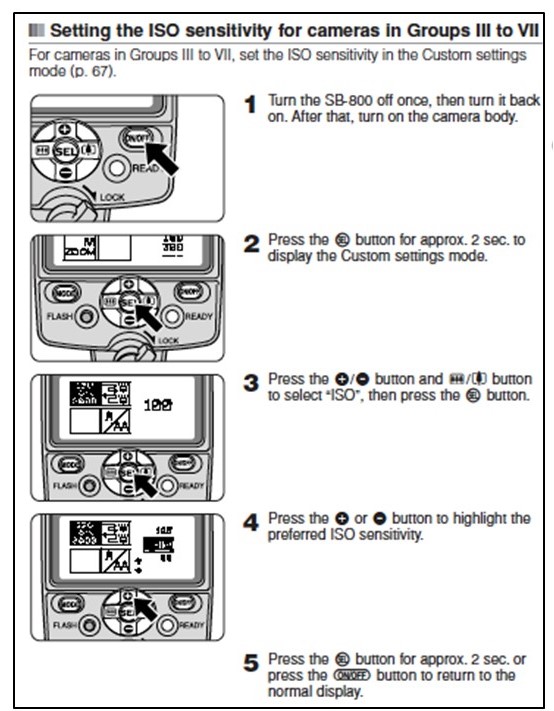
You may have noticed that many companies, like Canon and Ikea, now opt for pictorial formats for instructions. In so doing, they are attempting to minimize language barriers when offering their products in countries around the globe. They are also decreasing their costs for translating instructions and minimizing the potential for language errors and content inaccuracies that can occur through the translation process.
Text-based instructions, however, are still common. Perhaps more than in any other form of technical writing, visual aids or visual tutorials are crucial to text-based instructions. Sometimes, words simply cannot explain the step. Illustrations, photographs, screenshots, and the like are often critical to the readers’ ability to visualize what they are supposed to do. Be sure that the visual aids included with your instructions represent the image from the reader’s perspective. Typically, the visual aids are placed immediately below the step described in the text. Adding visual aids to instructions is about the only time that it is acceptable to be redundant in a technical document. Be sure to include sources for the images if you have not created them yourself.
Formatting Your Instructions
Since people rarely want to read instructions, but often have to, instructions should be formatted such that they are easy to read. Try to make your reader want to read them, or at least not resistant to the idea of consulting them. A highly readable format using headings, listing, passive space, and visual aids will allow readers who have figured out some of the instructions on their own to easily skip to the section where they are stuck. Use what you have learned about headings, lists, visuals, and passive space to create effective and readable instructions:
Headings: Normally, you’d want headings for any section in the document. For example, headings are needed for the background, equipment and supplies, a the actual instructions sections, and subheadings for the individual task phases within that last section. Always think: “What would make it easy for my reader to find the information they need?”
Lists: Similarly, instructions typically make extensive use of lists, particularly numbered vertical lists for the actual step-by-step explanations. Simple vertical lists or two-column lists are usually good for the equipment and supplies section. In-sentence lists are good whenever you give an overview of things to come.
Special Notices: You may have to alert readers to possibilities in which they may damage their equipment, waste supplies, cause the entire procedure to fail, injure themselves or others—even seriously or fatally. Companies have been sued for a lack of these special notices, for poorly written special notices, or for special notices that were out of place. See special notices for a complete discussion of the proper use of these as well as their format and placement within instructions.
Knowledge Check
As you reread and revise your instructions, check that they do the following:
- Provide an overview of content
- Indicate audience requirements
- Clearly describe the exact procedure to be explained
- Include a section listing equipment and supplies if necessary
- Include exact measurements and other values when required; for example, “a few drops” is far less specific than “.25 ml”
- Use various types of lists wherever appropriate; in particular, use numbered lists for sequential steps
- Use headings and subheadings to divide the main sections and subsections in a logical, coherent order
- Use special notices as appropriate
- Use visual aids to illustrate key actions, objects, and locations
- Provide additional supplementary explanation of the steps as necessary
References
Beilfus, M. (n.d.). Chapter 8: Technical instructions. Technical and professional writing genres. OSU Library. https://open.library.okstate.edu/technicalandprofessionalwriting/chapter/chapter-8/
Georgia State University. (2014). “Post #7: The importance of first impressions. http://sites.gsu.edu/techcomm-fall-2014/2014/10/10/post-7-the-importance-of-first-impressions/
McFarland, A. (2024, August 7). 5 Best AI SOP (Standard Operating Procedures) Generators in 2025 Unite.ai.
McMurrey, D. (1997-2022). Examples, cases, models. Online Technical Writing. https://mcmassociates.io/textbook/models.html
McMurrey, D. (1997-2022). Online technical writing: Special notices. https://mcmassociates.io/textbook/notices.html CC by 4.0 International License.
umnWritingStudies. (2013). Instruction documents. Writing effective steps [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h7Qn4GkpcLg&t=192s
Wood, O. (2013). What Makes a Good Instruction Manual. https://oliverwoodphotography.wordpress.com/2013/05/02/what-makes-a-good-instruction-manual/