Unit 46: Report Organization
Learning Objectives
 After studying this unit, you will be able to understand how reports are organized.
After studying this unit, you will be able to understand how reports are organized.
Introduction
Because reports vary by size, format, and function, writing them involves adjusting to the needs of the audience while respecting conventions and guidelines. Reports are typically organized around six key elements, the 5Ws + H:
- Whom the report is about and/or prepared for
- What was done, what problems were addressed, and the results, including conclusions and/or recommendations
- Where the subject studied occurred
- When the subject studied occurred
- Why the report was written (function), including under what authority, for what reason, or by whose request
- How the subject operated, functioned, or was used
Pay attention to these essential elements when you consider your stakeholders, or those who have an interest in the report. That may include the person(s) the report is about, whom it is for, and the larger audience of the business, organization, or industry. Ask yourself who are the key decision-makers reading the report, who the experts or technicians will be, and how executives and workers may interpret your words and images. (Business Communication for Success, 2015)
Organizational Pattern
Although reports have the same sections, the audience, purpose and content of a report will influence the report’s organizing pattern: direct or indirect.
Direct Pattern
Direct reports contain routine, nonsensitive information. Reports using this organizing pattern will present the most important findings first followed by facts, data and other explanatory details. Thus, the direct approach is most appropriate for informational reports. In addition, when the receiver is likely to be in agreement with and accepting of the report’s information and recommendations, the direct approach can also be applied to analytical reports. This approach allows the receiver to access relevant information in a quick, efficient and easy to follow manner.

Indirect Pattern
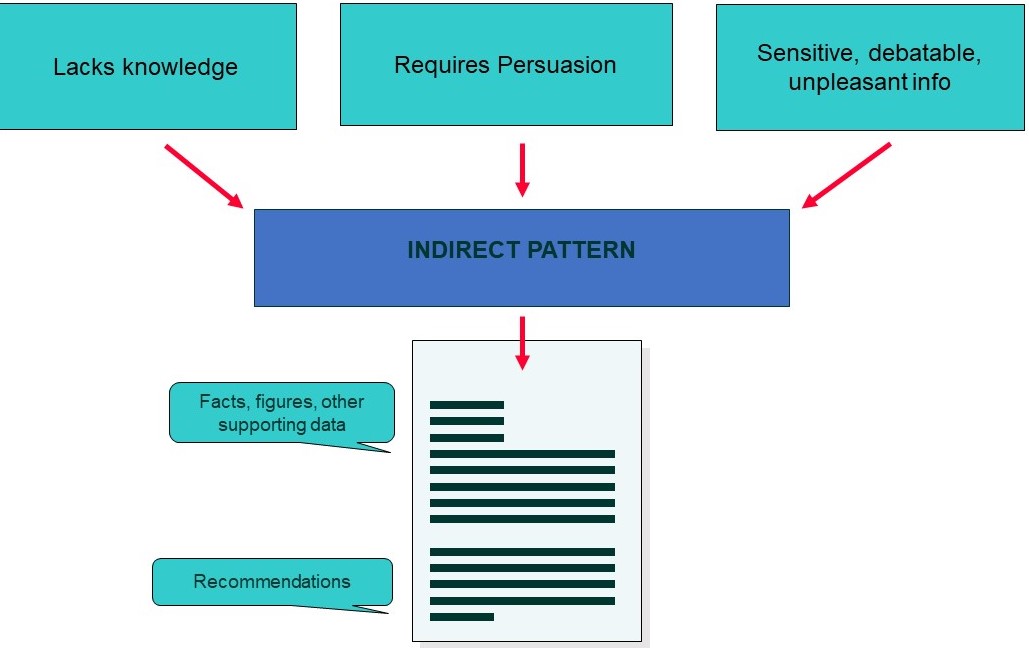
An indirect approach may contain sensitive, controversial, debated or unpleasant information. As a consequence, not all readers will be knowledgeable of, in agreement with, or accepting of the information and/or recommendations made in the report. For this reason, the indirect approach is used when the audience must be educated about or persuaded of the credibility of the information presented and the merits of the recommendations made. An indirect report presents the facts, data and other explanatory details before presenting its conclusions and recommendations. Since only analytical reports present recommendations, the indirect approach is used exclusively with analytical reports. (Business Communication Essentials, 2016; Communicating for Results, 2017)
Ordering Information
In addition to determining if your report will use the direct or indirect approach, information must also be organized to help the reader understand the information. Five of the more useful ways to organize information are presented below.
Table 46.1: Five Ways to Organize Information to Assist Reader Comprehension

References
Bovee, C., Thill, J., & Scribner, J. (2016). Business communication essentials (4th ed.). Toronto, ON: Pearson Canada Inc. Retrieved from http://www.pearsoncanada.ca/highered/product-showcase/new-solutions-for-core-foundations-from-pearson-canada/business-communication-essentials-fourth-canadian-edition-4e
Meyer, C. (2017). Communicating for results (4th ed.). Don Mills, ON: Oxford University Press. Retrieved from https://oup-arc.com/access/meyer-4e-student-resources#tag_case-studies.
USC. (2018). How to write a business report [Video]. Youtube. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V8uF1EoIneE&t=46s.

